In this article I will show how to measure carbon dioxide levels in your home. An important factor to test for when trying to measure indoor air quality (IAQ) is carbon dioxide. Tight homes with not enough ventilation and/or buildings with high occupancy are the usual candidates to having elevated carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, it is easy and low cost to measure CO2 levels. There is data from Lawrence Berkeley Lab that shows elevated indoor carbon dioxide (CO2) levels does impair cognitive abilities.
With that said it is important to remember carbon dioxide is only a part of a much larger indoor air quality picture. There are many contaminants that can be in the air in the following categories; particulate, biological, chemical / VOC, and gases. These are such things as dust mites, pollen, mold spores, mycotoxins, endotoxins, total VOCs, radon, and ozone just to name a few. These are all also influenced by temperature and humidity so only doing a carbon dioxide measurement is not going to give you enough data to have a good understanding of the state of your indoor air quality but it is a important data point.
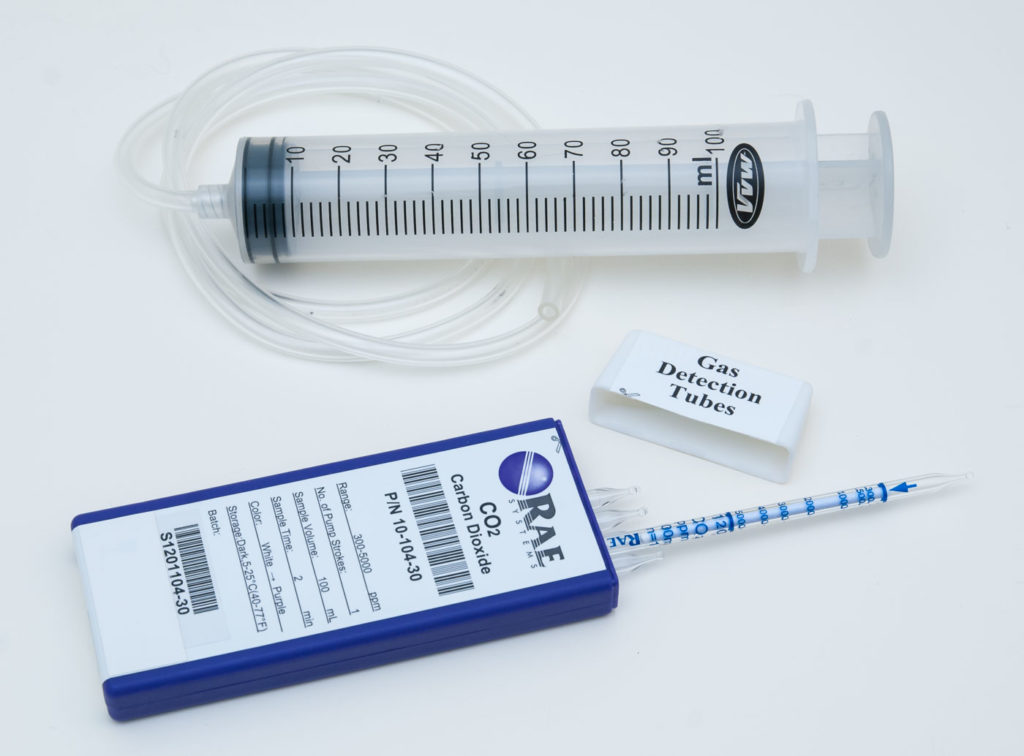
1. Carbon Dioxide Measurement Using Colorimetric Gas Detection Tubes
1.1 Carbon Dioxide Gas Detection Tubes
Colorimetric gas detector tube are used to measure the amount of a target gas present in an environment when a known volume of that environment’s air is pumped through a tube. The tube typically has a layer which indicates the analyte (target gas to measure) by changing colour, depending on the amount of the gas which has passed through the tube the length of the zone which has changed color will be different.
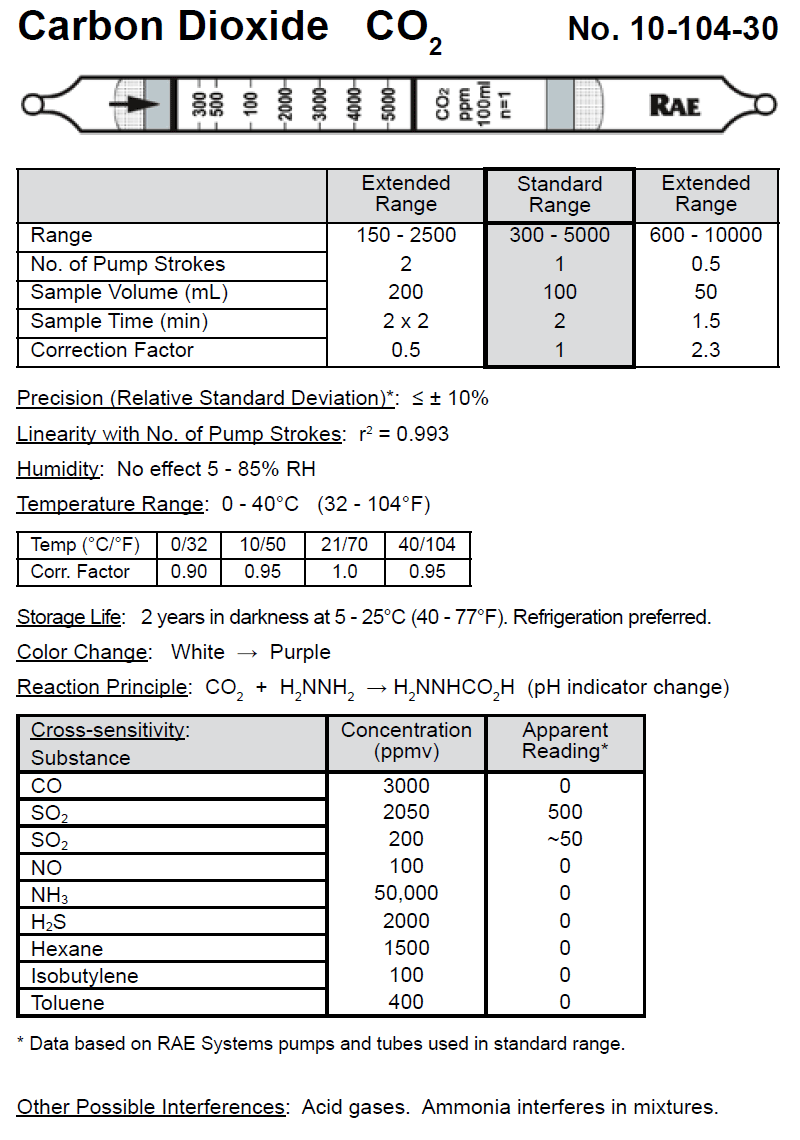
The best value carbon dioxide tube I found was RAE Systems 10-104-30, 300-5000 ppm gas detection tube. It comes in a 10 pack which costs $35 plus shipping. With all supplies needed it should come out to about $5 per test.
1.2 Manual Hand Pump
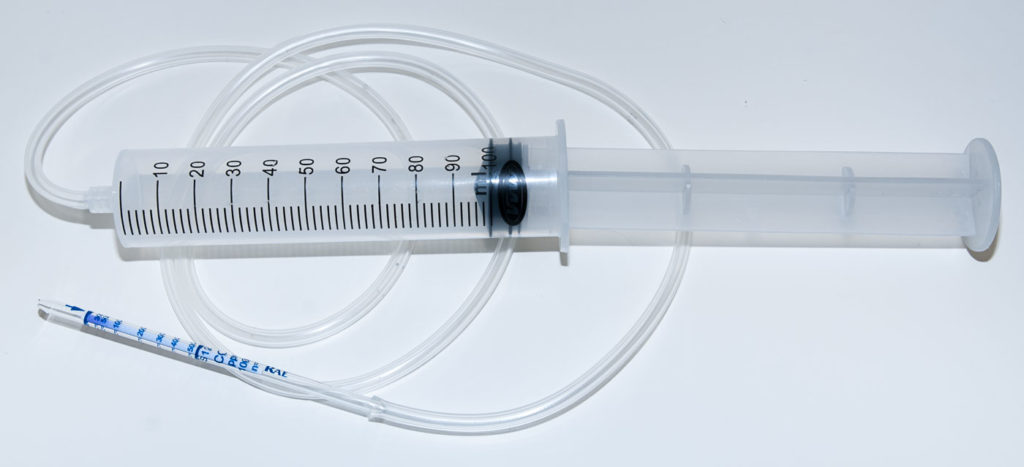
Normally what is used to pump the air through this carbon dioxide detector tube is a professional hand pump matched to the same manufacture of the tubes which will accurately pump 100 mL of air through the test tube. These pumps have nice features like indicators to show when the tube is no longer under vacuum, latches to hold the pump plunger, settings for 50 mL or 100 mL strokes, and stroke counters for tubes that need more than 100 mL of air pumped through them. These pumps are an absolute requirement for a professional doing these measurements for a client or for traceability. Most people reading this article are going to be just a DIY’er or a homeowner trying to get a general idea of your indoor CO2 levels so a simple 100mL syringe can be used. This will likely not yield as accurate results but should not be an issue for most non-professional uses.
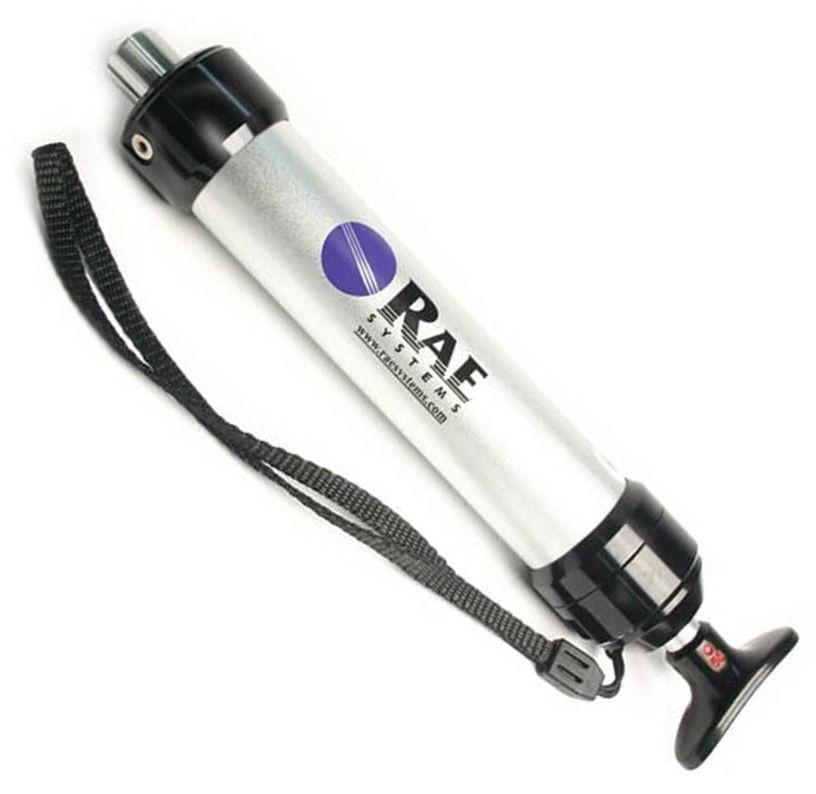

Professional Manual Hand Pump
Cost: ~$200-$400 for most
1.3 Measuring Carbon Dioxide Testing Procedure
While performing the test make sure not to breath on or around the tube as it will falsely increase your indoor carbon dioxide measurement
Using a 100 mL syringe
- Connect air tubing to syringe (pump)
- Break both ends off carbon dioxide test tube off
- Push air tubing over the test tube making sure the airflow direction arrow is pointing towards the end you connected the tube to
- Slowly pull syringe to 100 mL mark on syringe and hold while air is getting pulled through tube, this will take 1-2 minutes
- Read tube reading immediately
Using a professional hand pump
- Set the pump to a 100 mL stroke (most pumps can do either 50 mL or 100 mL strokes)
- Break both ends of the carbon dioxide test tube off
- Insert CO2 test tube into the hand pump with the air flow arrow pointing towards the pump
- Tighten the pump to tightly hold the tube if your pump has this
- Pull pump handle and wait 2 minutes or until vacuum indicator on pump indicates the tube is not under vacuum anymore
- Read tube reading immediately
1.4 Reading the Carbon Dioxide Level From Tube

The above detection tube has a reading of about 500 ppm. The best way to read these tubes is to place them next to an unused tube and compare. If there is a gradient you want to measure towards the end of the gradient. In the above tube you can see the region from about 500 ppm to right after 1000 ppm is slightly darker, this can be ignored.
2. Carbon Dioxide CO2 Reference Levels
| Level | Reference |
| 350 – 450 ppm | Typical outdoor CO2 level |
| 1000 ppm | ASHRAE 62-1989. ASHRAE 62-1999 standard recommends maintaining under 700 ppm CO2 differential between outdoor and indoor air. “This level is not considered a health risk but is a surrogate for human comfort (odor)” as elevated CO2 levels are closely related to the number of occupants and their activity level which can be a good correlation with the amount of body odor. |
| 2,500 ppm | Lawrence Berkeley Lab study which assessed cognitive function assessed using a computer-based program called the Strategic Management Simulation (SMS) at different indoor air levels of CO2. Found a CO2 level of 2,500 ppm diminishes test subjects cognitive function to “dysfunctional” on the taking initiative and thinking strategically indexes. [source] |
| 30,000 ppm | OSHA less than 15-minute Short-Term Exposure Limit (STEL) |
| 40,000 ppm | Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH) (greater than 5 minutes) |
| ~50,000 ppm | 30-minute LC (Lethal Concentration) in humans, causes unconsciousness |
| 70,000 – 100,000 ppm | Few minute LC (Lethal Concentration) in humans, causes unconsciousness |
Related Posts:
– DIY Indoor Formaldehyde Levels Measurement

Thanks for the video tutorial. It seems that whole process is quite easy and can be copied at home by many people. Hope you can share more such material for testing indoor chemicals.
I think I at least am being poisoned by carbon dioxide in my apartment maybe other tenets to 120 north cottonwood st apartment 35 woodland CA 95695
U good Lisa?
Before we talk about CO2 as pollutant or a health hazard, let’s dwell on Indoor Air Quality (IAQ). IAQ is a term coined to represent the air quality of occupied buildings, which can be offices, factories, showrooms, malls, schools, colleges so on and so forth. Carbon dioxide is one of the most important gases effecting IAQ.
interested does it test for carbon mioxide etc as well
Does co2 rise in an apartment building? I just moved in here and I am on the highest floor. I can’t just leave it’s not that easy but I tested with a free metre from the library and I already know the CO2 was very high. It was giving me alerts not sure what to do. Would a llower floor be safer.